Rayan Nik Tajhiz Company
Red Hat OpenShift, a facilitating tool for application developers

Red Hat OpenShift
Red Hat OpenShift is a container base platform, and Red Hat has developed and presented it based on the concept of Kubernetes. Open Shift helps software developers develop and release their applications without getting bogged down in the details.
Red Hat OpenShift is the same OS owned by Red Hat company, on which containers and Kubernetes are located, and Red Hat company experts test all containers, Kubernetes, and commands and provide them by fixing all the flaws so that organizations can safely use them.
Red Hat OpenShift is a container base platform, and Red Hat has developed and presented it based on the concept of Kubernetes. Open Shift helps software developers develop and release their applications without getting bogged down in the details.
When OpenShift and Kubernetes come together, they increase operational speed and accuracy for developers. Without the help of these two, all the programming steps must be done manually by the development team; The developers are involved in commanding, testing, and related complex details. However, OpenShift has made this process simpler and faster, making it easy to launch applications.
Container
Since Red Hat OpenShift is based on the concept of a container, it is necessary to understand this concept first. In the past, the hardware structure comprised several layers:
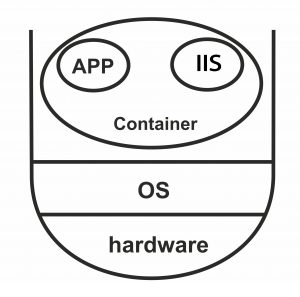
Here, after the OS layer, the hypervisor layer was located, then the VMs were placed, and each application was installed separately on each of these items. To install any IIS or APP, it was necessary to install a separate VM and an OS. Because of the existence of several layers, the performance and speed of the system decreased. The reason for introducing the container was to remove some layers and not need to install Hypervisor and separate OSes. Here, each APP is installed directly on the container and improves the performance of the system. Here, all containers use the same operating system. In the following, the structure of hardware with a container is shown:
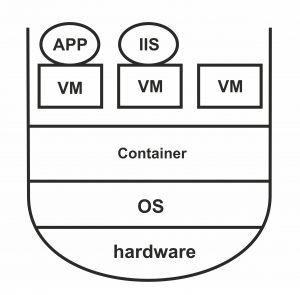
OpenShift
The container eliminated the problem of installing the OS and the hypervisor layer separately. However, if the application or the program to be used were of different types, different problems would come up. For example, if one application is Windows and the other is Linux, using and setting up both on the same hardware might be complicated. That’s why OpenShift entered the market to solve this big challenge for developers and programmers: There should be no problem installing an IIS based on Windows and an Apache based on Linux, and it is possible to implement both in one operating system. This way, if developers want to operate a container and install OpenShift, they can run three applications at the same time.
If customers use the container and get OpenShift they can support three different systems, regardless of whether it is based on Windows or Linux.
To simplify this concept, it can be said that OpenShift provides an Apache container and a database container and, in the same way, you do not need to install a separate OS or hypervisor so that you can easily use different systems in one hardware.
Now the main question is that when the number of applications increases, how do containers help to increase system performance?
In this situation, the containers automatically create a container system and run the next IIS on the same container and divide the traffic between them. Containers create fast and powerful performance and act as load balancing.
Kubernetes
The next step was the challenge that organizations faced in managing containers. Because the number of containers increases, managing them is a challenge. To solve this challenge, Google introduced the Kubernetes product so that all containers can be managed. In summary, it can be said that to improve the performance of a system, it is possible to optimize the system by going through the following steps in the discussion of launching various applications and also in the discussion of managing these containers:
Providing the desired hardware
Installing CentOS
Running the container
Ultimately, managing these with Kubernetes
Red Hat OpenShift
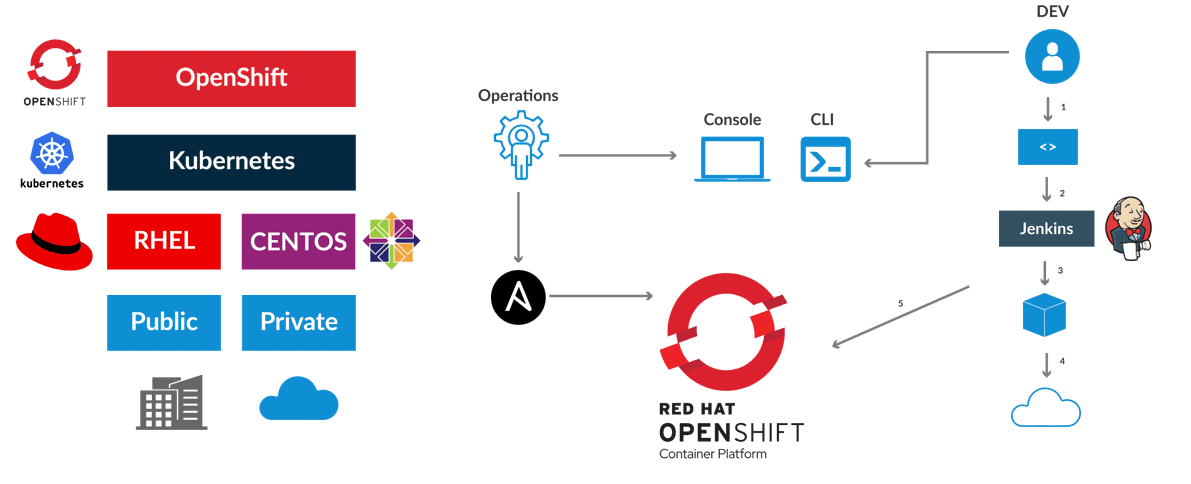
The thing about working with Kubernetes is that you have to manage all the activities by typing a command, and this creates new difficulty and complexity, and it is time-consuming as well. To solve this problem, Red Hat company has introduced Red Hat OpenShift. To help the developers, all the commands available and required by the organizations have been checked and tested, and then all of them have been included in this product. That is, an Enterprise Kubernetes is offered that is web-based. To solve this complexity and time-consuming, Red Hat Company has provided a complete menu of all commands and made it available on the web so that all companies can use these commands as quickly as possible. Here, instead of developers writing commands repeatedly, they can refer to the Red Hat OpenShift web menu and execute it quickly time.
Another feature of Red Hat OpenShift is to help organizations operate as a Hybrid Cloud. It means having a combination of VMs on the cloud platform and having a part of them on their site, which is also called on-premise. Red Hat OpenShift makes it possible to create more applications and services with the same available host and resources because it eliminates the need to install the OS separately. In short, the Red Hat OpenShift product is like an operating system that has provided all products, including containers and Kubernetes, and supports them so that you can place any type of database, such as SQL and MYSQL, on containers and use them.

